
It can alter both sources and sinks of greenhouse and chemically important trace gases (e.g., carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, carbonyl sulfide, ozone, and possibly other gases). Increases in UVB radiation could affect terrestrial and aquatic biogeochemical cycles: These changes can have important implications for plant competitive balance, herbivory, plant diseases, and biogeochemical cycles. the decline in plant productivity would in turn affect soil erosion and the carbon cycle. flowering and photosynthesis in plants,. timing of developmental phases and secondary. how nutrients are distributed within the plant. Despite mechanisms to reduce or repair these effects and an ability to adapt to increased levels of UVB, plant growth can be directly affected by UVB radiation. UVB radiation affects the physiological and developmental processes of plants. UVB has been linked to the development of cataracts, a clouding of the eye’s lens. 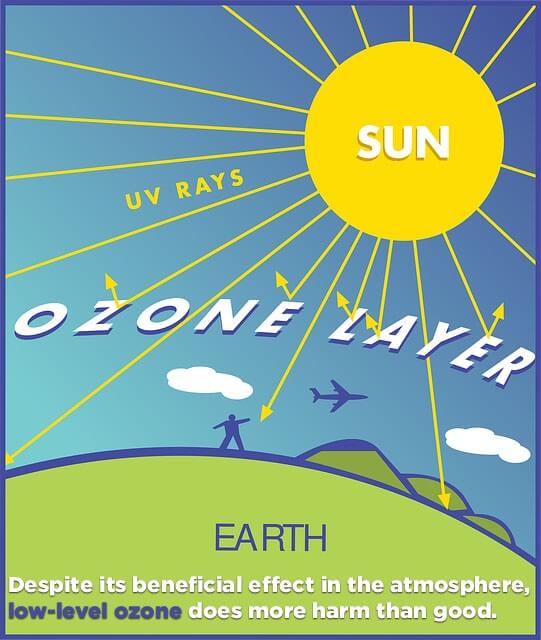
Plays a major role in malignant melanoma development.Laboratory and epidemiological studies demonstrate that UVB causes: Ozone layer depletion increases the amount of UVB that reaches the Earth’s surface. Major volcanic activity can also contribute to ozone depletion. But this has been found to cause not more than 1-2% depletion of the ozone layer and the effects are also thought to be only temporary. There are a few natural causes of ozone depletion are also like Sun-spots and stratospheric winds.
 One of the largest such holes appears annually over Antarctica between September and November.
One of the largest such holes appears annually over Antarctica between September and November. 
Usually, ozone holes form over the Poles during the onset of the spring seasons.
Ozone holes refer to the regions of severely reduced ozone layers. This has led to the formation of what is called the ‘ozone hole’.
In atmospheric regions over Antarctica, the ozone layer is significantly thinner, especially in the spring season. It is estimated that about 5-9% thickness of the ozone layer has decreased, increasing the risk of human over-exposure to UV radiation owing to the outdoor lifestyle. This has led to an increase in UV radiation reaching the earth. In the mid-latitudes, for example, over Australia, the ozone layer is thinned.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
